ISSN: 1839-9940
J Genomics 2024; 12:58-70. doi:10.7150/jgen.93243 This volume Cite
Research Paper
The impact of Elaeagnus angustifolia root exudates on Parafrankia soli NRRL B-16219 exoproteome
1. Department of Biological and Chemical Engineering USCR Molecular Bacteriology and & Genomics, National Institute of Applied Sciences and Technology, University of Carthage, Tunis, Tunisia.
2. Département Médicaments et Technologies pour la Santé (DMTS), CEA, INRAE, Université Paris-Saclay, SPI, 30200 Bagnols sur Cèze, France.
3. Higher Institute of Applied Biological Sciences, Laboratory of Bioresources, Environment, and Biotechnology, University of Tunis El Manar, Tunis, Tunisia.
4. Higher Institute of Biotechnology of Sidi Thabet, University of La Manouba, Sidi Thabet, Tunisia.
Abstract
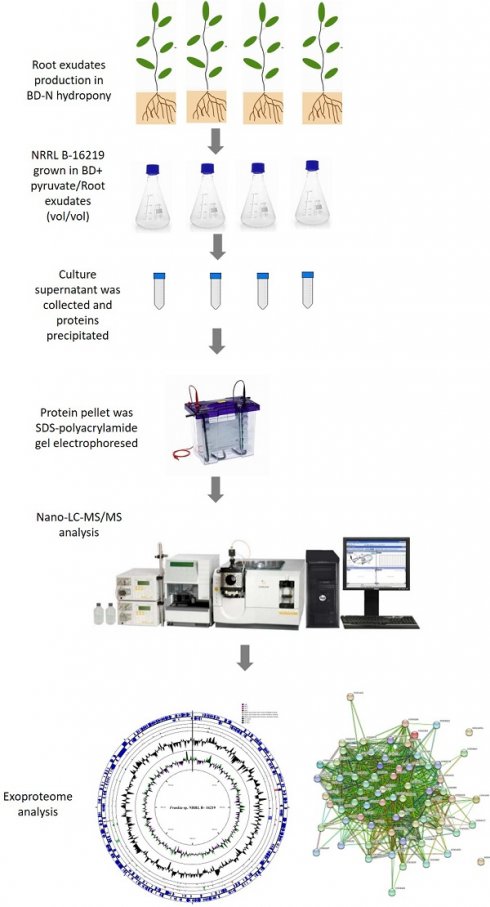
Root exudates from host plant species are known to play a critical role in the establishment and maintenance of symbiotic relationships with soil bacteria. In this study, we investigated the impact of root exudates from compatible host plant species; Elaeagnus angustifolia on the exoproteome of Parafrankia soli strain NRRL B-16219. A total of 565 proteins were evidenced as differentially abundant, with 32 upregulated and 533 downregulated in presence of the plant exudates. Analysis of the function of these proteins suggests that the bacterial strain is undergoing a complex metabolic reprogramming towards a new developmental phase elicited in presence of host plant root exudates. The upregulation of Type II/IV secretion system proteins among the differentially expressed proteins indicates their possible role in infecting the host plant, as shown for some rhizobia. Additionally, EF-Tu, proteins upregulated in this study, may function as an effector for the T4SSs and trigger plant defense responses. These findings suggest that Parafrankia soli may use EF-Tu to infect the actinorhizal host plant and pave the way for further investigations of the molecular mechanisms underlying the establishment of symbiotic relationships.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact