ISSN: 1839-9940
J Genomics 2023; 11:14-19. doi:10.7150/jgen.80829 This volume Cite
Research Paper
Draft Genomes of Halophilic Chromohalobacter and Halomonas Strains Isolated from Brines of The Carpathian Foreland, Poland
1. Department of Molecular Microbiology, Faculty of Biology and Environmental Protection, University of Lodz, Lodz, Poland
2. Biobank Lab, Department of Oncobiology and Epigenetics, Faculty of Biology and Environmental Protection, University of Lodz. Lodz, Poland
3. Screening of Biological Activity Assays and Collection of Biological Material Laboratory, Wroclaw Medical University Biobank, Faculty of Pharmacy, Wroclaw Medical University, Wroclaw, Poland
Abstract
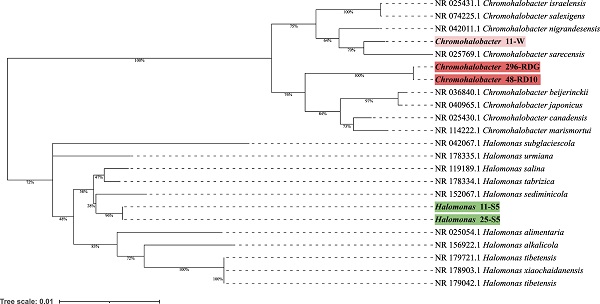
Chromohalobacter and Halomonas are genera of bacterial microorganisms belonging to the group of halophiles. They are characterized by high diversity and the ability to produce bioproducts of biotechnological importance, such as ectoine, biosurfactants and carotenoids. Here, we report three draft genomes of Chromohalobacter and two draft genomes of Halomonas isolated from brines. The length of the genomes ranged from 3.6 Mbp to 3.8 Mbp, and GC content was in the 60.11%-66.46% range. None of the analysed genomes has been assigned to any previously known species of the genus Chromohalobacter or Halomonas. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that Chromohalobacter 296-RDG and Chromohalobacter 48-RD10 belonged to the same species, and Chromohalobacter 11-W is more distantly related to the other two analysed strains than to Chromohalobacter canadensis. Halomonas strains 11-S5 and 25-S5 were clustered together and located close to Halomonas ventosae. Functional analysis revealed BGCs related to ectoine production in all genomes analysed. This study increases our overall understanding of halophilic bacteria and is also consistent with the notion that members of this group have significant potential as useful natural product producers.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact