ISSN: 1839-9940
J Genomics 2019; 7:31-45. doi:10.7150/jgen.32164 This volume Cite
Review
Metadata Analysis Approaches for Understanding and Improving the Functional Involvement of Rumen Microbial Consortium in Digestion and Metabolism of Plant Biomass
1. Department of Biology, Lakehead University, 955 Oliver Road, Thunder Bay, Ontario, P7B 5E1, Canada.
2. Research Center in Applied Chemistry (CEPESQ), Department of Chemistry, Universidade Federal do Paraná, P. O. Box 19032, Curitiba, Paraná, 81531-980, Brazil.
Abstract
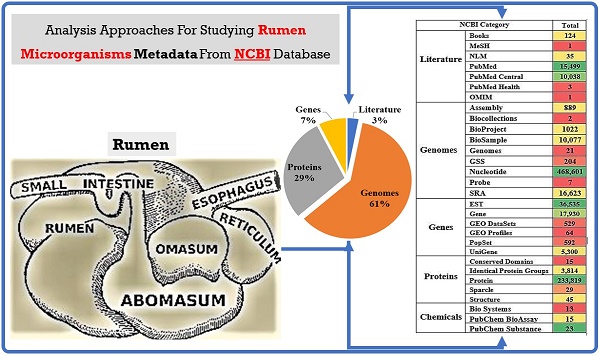
Rumen is one of the most complex gastro-intestinal system in ruminating animals. With bountiful of microorganisms supporting in breakdown and consumption of minerals and nutrients from the complex plant biomass. It is predicted that a table spoon of ruminal fluid can reside up to 150 billion microorganisms including various species of bacteria, fungi and protozoa. Several studies in the past have extensively explained about the structural and functional physiology of the rumen. Studies based on rumen and its microbiota has increased significantly in the last decade to understand and reveal applications of the rumen microbiota in food processing, pharmaceutical, biofuel and biorefining industries. Recent high-throughput meta-genomic and proteomic studies have revealed humongous information on rumen microbial diversity. In this study, we have extensively reviewed and reported present-day's progress in understanding the rumen microbial diversity. As of today, NCBI resides about 821,870 records based on rumen with approximately 889 genome sequencing studies. We have retrieved all the rumen-based records from NCBI and extensively catalogued the rumen microbial diversity and the corresponding genomic and proteomic studies respectively. Also, we have provided a brief inventory of metadata analysis software packages and reviewed the metadata analysis approaches for understanding the functional involvement of these microorganisms. Knowing and understanding the present progress on rumen microbiota and performing metadata analysis studies will significantly benefit the researchers in identifying the molecular mechanisms involved in plant biomass degradation. These studies are also necessary for developing highly efficient microorganisms and enzyme mixtures for enhancing the benefits of cattle-feedstock and biofuel industries.
Keywords: Ruminating animals, Ruminal fluid, Microbiota, Genomic, Proteomic, Bacteria, Fungi, Protozoa.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact