ISSN: 1839-9940
J Genomics 2018; 6:9-19. doi:10.7150/jgen.23222 This volume Cite
Research Paper
Constructing a 'Chromonome' of Yellowtail (Seriola quinqueradiata) for Comparative Analysis of Chromosomal Rearrangements
1. Department of Life Sciences, Graduate School of Bioresources, Mie University, Tsu city, Mie Prefecture, Japan;
2. National Research Institute of Aquaculture, Fisheries Research Agency, Tamaki-cho, Mie Prefecture, Japan.
Abstract
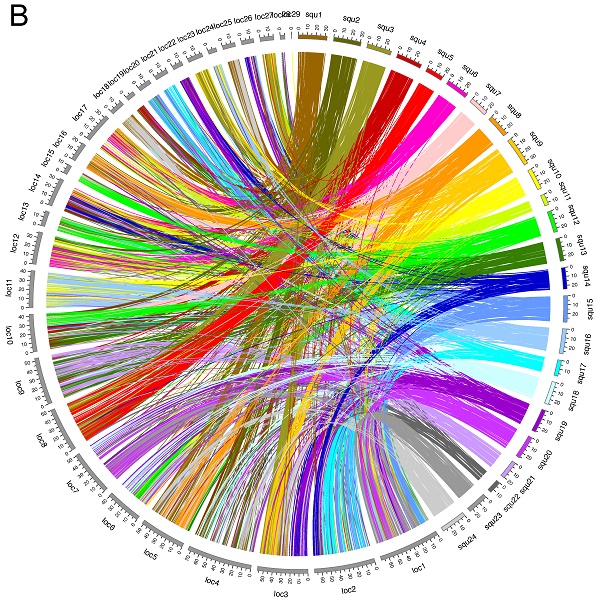
To investigate chromosome evolution in fish species, we newly mapped 181 markers that allowed us to construct a yellowtail (Seriola quinqueradiata) radiation hybrid (RH) physical map with 1,713 DNA markers, which was far denser than a previous map, and we anchored the de novo assembled sequences onto the RH physical map. Finally, we mapped a total of 13,977 expressed sequence tags (ESTs) on a genome sequence assembly aligned with the physical map. Using the high-density physical map and anchored genome sequences, we accurately compared the yellowtail genome structure with the genome structures of five model fishes to identify characteristics of the yellowtail genome. Between yellowtail and Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes), almost all regions of the chromosomes were conserved and some blocks comprising several markers were translocated. Using the genome information of the spotted gar (Lepisosteus oculatus) as a reference, we further documented syntenic relationships and chromosomal rearrangements that occurred during evolution in four other acanthopterygian species (Japanese medaka, zebrafish, spotted green pufferfish and three-spined stickleback). The evolutionary chromosome translocation frequency was 1.5-2-times higher in yellowtail than in medaka, pufferfish, and stickleback.
Keywords: Acanthopterygii, chromosome evolution, de novo assembly, radiation hybrid map, synteny analysis, whole-genome sequencing

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact