ISSN: 1839-9940
J Genomics 2016; 4:42-47. doi:10.7150/jgen.16156 This volume Cite
Short Research Communication
Whole Genome Sequence Analysis of an Alachlor and Endosulfan Degrading Micrococcus sp. strain 2385 Isolated from Ochlockonee River, Florida
1. Environmental Biotechnology and Genomics Laboratory, School of the Environment, 1515 S. Martin Luther King Jr. Blvd., Suite 305B, FSH Science Research Center, Florida A&M University, Tallahassee, FL- 32307, USA.
2. Department of Microbiology, Central Laboratory for Environmental Quality Monitoring (CLEQM), National Water Research Center, Egypt.
3. Department of Agricultural, Food and Nutritional Science, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB T6G2P5, Canada.
Abstract
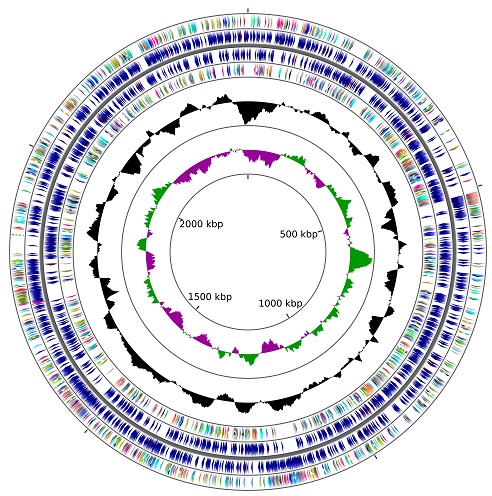
We recently isolated Micrococcus sp. strain 2385 from Ochlockonee River, Florida and demonstrated potent biodegradative activity against two commonly used pesticides- alachlor [(2-chloro-2`,6`-diethylphenyl-N (methoxymethyl)acetanilide)] and endosulfan [(6,7,8,9,10,10-hexachloro-1,5,5a,6,9,9a-hexahydro-6,9methano-2,3,4-benzo(e)di-oxathiepin-3-oxide], respectively. To further identify the repertoire of metabolic functions possessed by strain 2385, a draft genome sequence was obtained, assembled, annotated and analyzed. The genome sequence of Micrococcus sp. strain 2385 consisted of 1,460,461,440 bases which assembled into 175 contigs with an N50 contig length of 50,109 bases and a coverage of 600x. The genome size of this strain was estimated at 2,431,226 base pairs with a G+C content of 72.8 and a total number of 2,268 putative genes. RAST annotated a total of 340 subsystems in the genome of strain 2385 along with the presence of 2,177 coding sequences. A genome wide survey indicated that that strain 2385 harbors a plethora of genes to degrade other pollutants including caprolactam, PAHs (such as naphthalene), styrene, toluene and several chloroaromatic compounds.
Keywords: Alachlor, Endosulfan, Biodegradation, Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS), Micrococcus.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact